Using Google Search Console’s Page indexing report, you can get a full list of all the URLs that Google has discovered on your website and their current status in the index. URLs that are not in Google’s index cannot be ranked in Google search results.
For non-experts, Google says that you can ignore this report if your site has fewer than 500 pages. In a short beginner’s guide to using Search Console, Has Google found all your pages? it also stressed that you should not expect all URLs in a large site to be indexed.
Discovering the Page indexing report in Search Console
On the Page indexing report featured below, we can see that 2.075 pages have been indexed (2.08K in green), but 6.008 pages (6.01K in gray) are not indexed. The chart at the top of the screen shows how this situation has evolved over time. In this example, the proportion of indexed / not indexed pages has been regular over the past 3 months.
This may not necessarily be a problem. As we saw in a previous chapter, the sitemap that lists all the pages, posts and category pages for this website only contains 979 URLs. Check the errors for your sitemap first before delving into to the full report shown below.
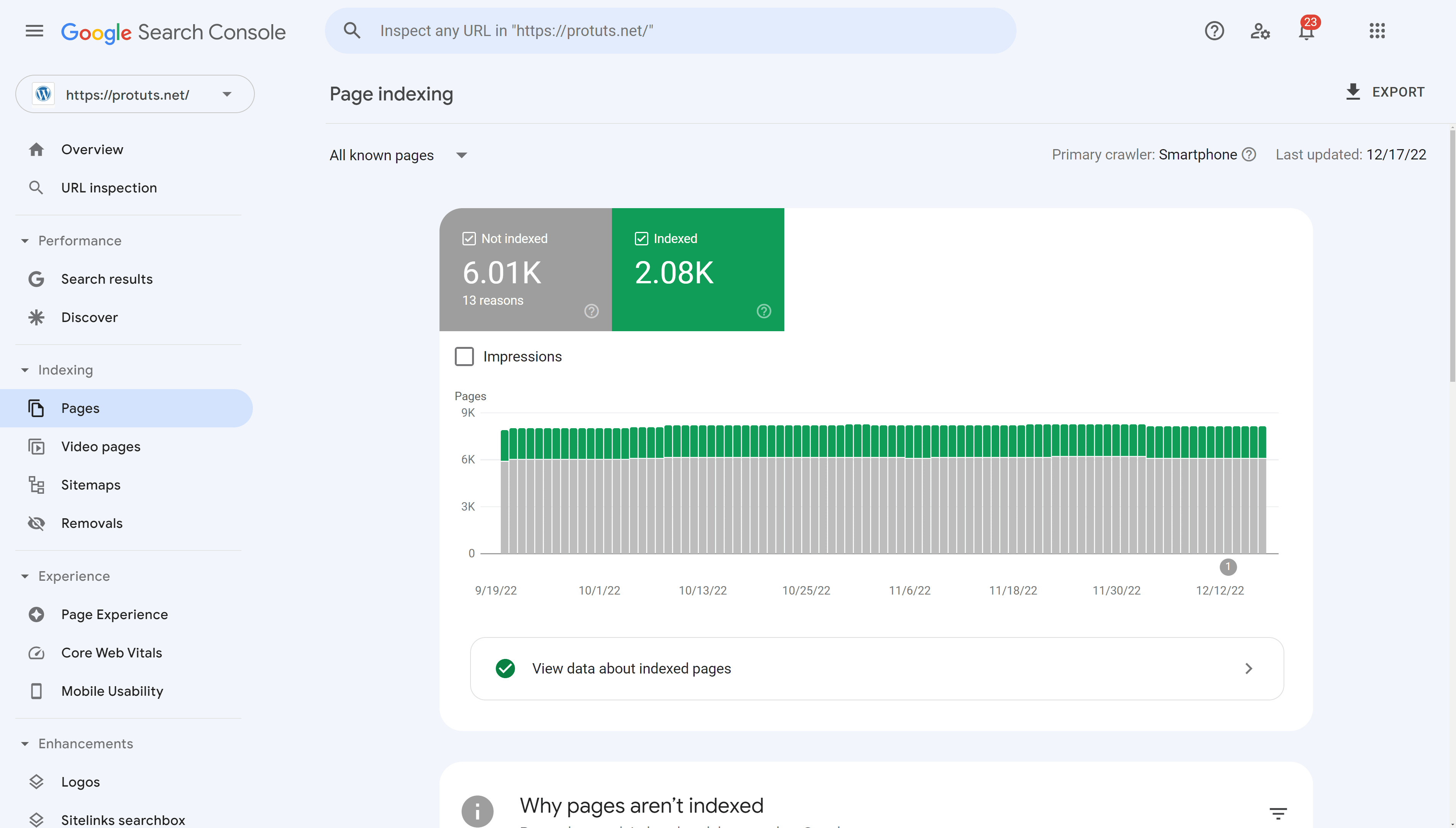
On the full report the chart, further down the page, Google lists the reasons why URLs are not indexed. This shows the source (whether the reason is caused by the website or Google), the validation status of the problem, the trend over time and the number of pages affected by the problem.
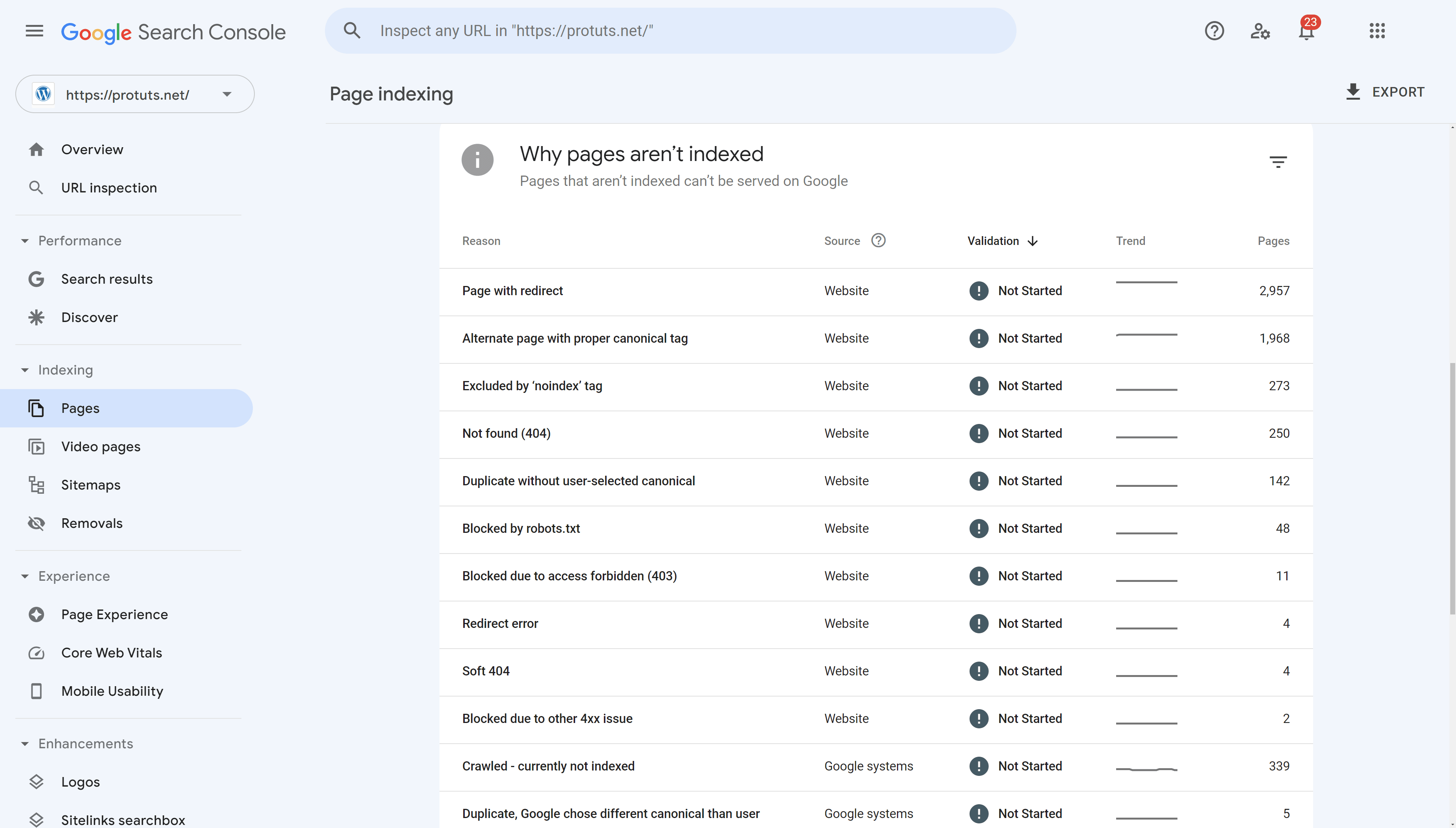
By clicking on each reason, you can see a complete report featuring a short description of the problem and a link LEARN MORE that will take you to the appropriate section of the Google Search Console Help documentation. You can also click on the VALIDATE FIX button in this top section if you have resolved the issue on the website.
Below this first section there is a chart showing the evolution of the problem over time and below that again a section listing examples of pages with the problem.
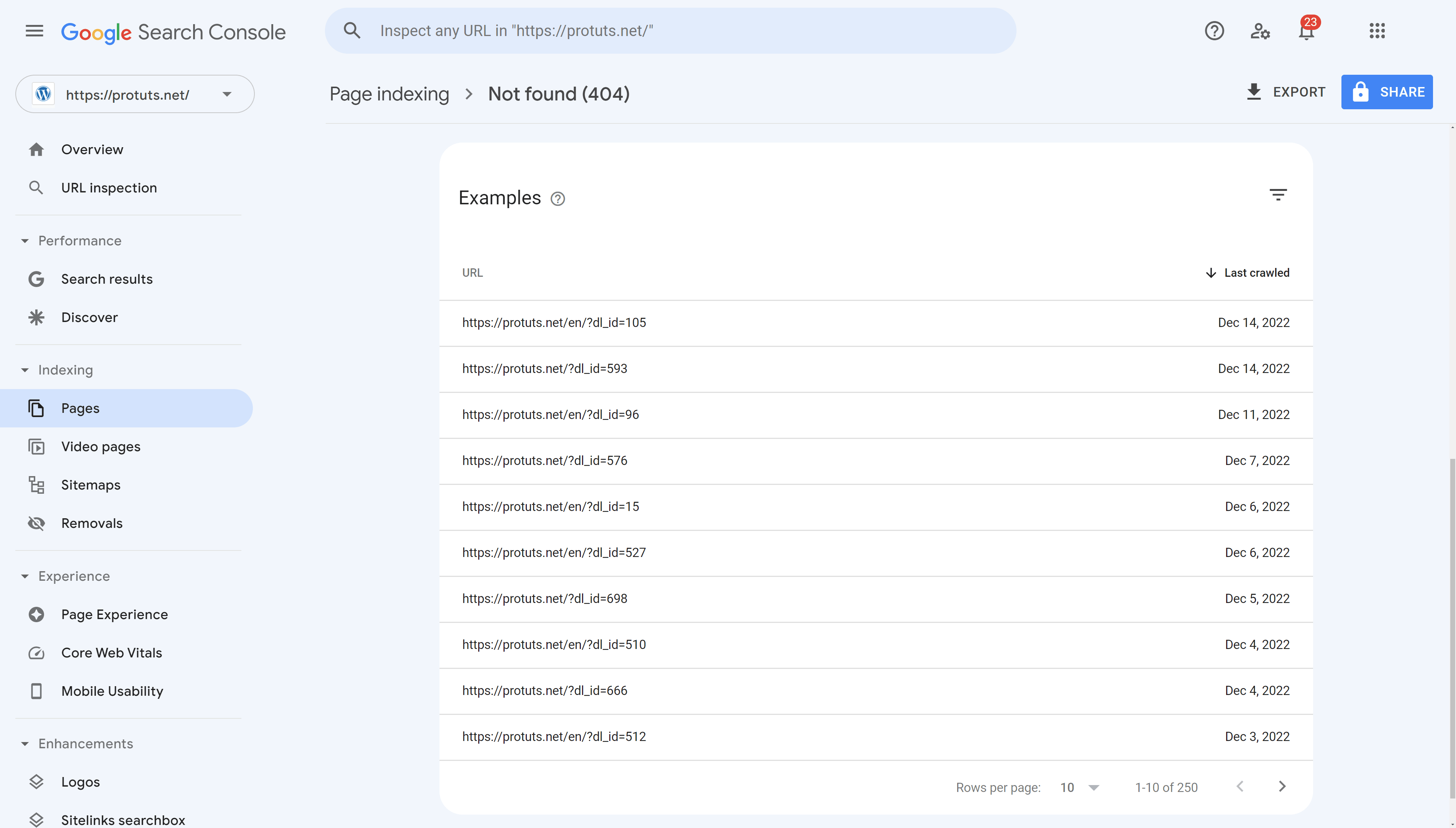
By passing your mouse cursor over each row, you will see icons appear that allow you to Copy the URL, Open in a new tab or Inspect URL. You can also click on the row to display a popup that will allow you to inspect the URL or test that robots.txt is not blocking Google from crawling it.
Common errors in the Page indexing report
Looking into some of the important errors on this website here are some ideas on how you can troubleshoot some common indexing problems:
- Not found (404) – these are pages that Google has found by crawling your website or other websites, but these pages did not exist the last time it tried to crawl them (a URL that does not exist returns a 404 status code). Best practice is to make sure you are not linking to pages that return 404 errors from your website. The majority of the not found pages in the screen shot above are URLs with the dl_id variable and correspond to download links provided on the site. These need to be corrected to make sure they do not point to 404 errors or removed. It may be normal to have a lot of not found pages when taking into account historic versions of your site. There is no way to force Google to forget pages that it once discovered, but you can redirect old URLs to new ones.
- Blocked due to access forbidden (403) – A 403 is another error like 404 meaning that a page no longer exists. You can treat these errors in the same way as Not found (404) errors.
- Blocked due to unauthorized request (401) – Another not found error that can occur when Google encounters a request for authorization (login, password) when trying to access a URL. Test any example URLs to make sure that you are also getting an authorization request, try un incognito mode to make sure that you test these pages without being connected to the website. If you can access URLs marked “Blocked due to unauthorized request (401)” without authorization, it may mean that a site administrator has blocked Google while trying to protect the site from being scraped by other crawlers. See this resource for Verifying Googlebot and other Google crawlers.
- Pages with redirect – these are URLs that Google has found for your website, but which now redirect to other URLs. For example, https://protuts.net/supprimer-bouton-/ redirects to https://protuts.net/supprimer-bouton-affichage-bureau-windows-7/. This probably happened after this post’s permalink was changed. This is not a problem if the old URL is no longer being used. It may be worth inspecting the URL for the errors that were discovered the most recently to see if a Referring page is listed. Best practice is to make sure that you are not linking internally using redirected links.
- Excluded by noindex tag – SEO plugins for WordPress like SEOPress allow you to indicate that certain pages are “noindex”, meaning that you don’t want Google to index them – you explicitly don’t want Google to include them in search results. This report shows pages that Google has discovered but is instructed not to index. Some site owners will noindex author pages, for example, to avoid duplication between author pages, categories and posts.
- Duplicate without user-selected canonical – This error message indicates that Google discovered pages that contained the same content as other pages on another URL. It could occur simply if you duplicated a post in WordPress and published it with two separate permalinks. Best practice is to always set a canonical URL for every page you publish to avoid this error being generated incorrectly by variables. This tag is added automatically if you use SEOPress. In the case where you do duplicate the same content on two different permalinks, you should use the canonical tag in the SEO metabox to index the version you want Google to prefer. This error message “without user-selected canonical” means that Google did not find a canonical tag and had to decide which URL should be preferred.
The examples above cover most “Not indexed” errors in Google Search Console. For a full list of possible errors and warning with further explanations see Google’s Page Indexing report help page.
When you first set up Google Search Console, spend time going through these error reports to see if you can resolve the indexing issues. Use the VALIDATE FIX button when you have resolved issues. Come back regularly to the reports to make sure there is not a spike of new issues. Normally you will be informed by email by Google if there is a important increase in indexing issues.





