Images are an important part of the web and, not surprisingly, they are an important part of search too. According to a 2019 study assembled by SparkToro, 21.5% of search results in the US are in Google Images. New features added by Google (including Google Lens) may also mean that image searches – including searching by images rather than words – will become more popular in the future.
Images are also used to enhance snippets in the more traditional Google Web Search results. The visual impact of images in SERPs can be an important factor in attracting attention and generating traffic.
There are also indications (such as the first Product Reviews Update in 2021) that Google also now uses AI to understand the content of images and uses this understanding as part of the ranking algorithm.
But images can also cause problems for SEO. They are often the major cause of slow page speed and are sometimes used where text would have been more appropriate. It is therefore vitally important to understand how to do Image SEO to get the most from search engines.

How Google Images search works
Google users search for images using a dedicated search engine that can be an extra source of traffic for your website.
There are 1.2 million searches in Google every month in the US for the keyword “Google Images” and there is an Images link at the top of the Google.com home page. Many other users, however, will type a search query into Google Web Search first and then click on the Images tab at the top of the page to get the dedicated Google Images results page.
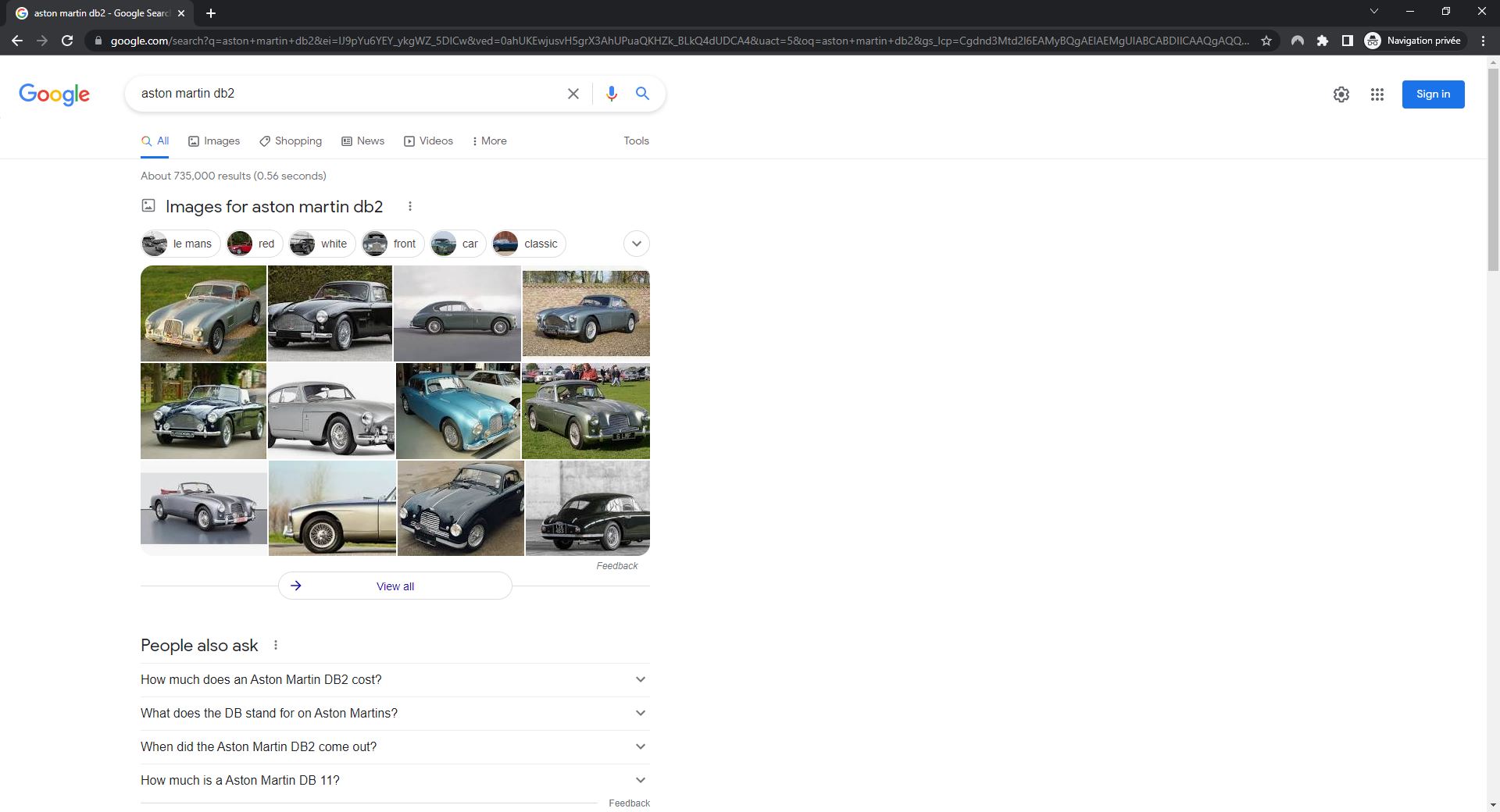
If image search is popular for a query, Google will show an Images for preview box in search results. Clicking on View All at the bottom of this panel will send users to the Google Images results. Clicking on an image will send users to an image preview (see below).
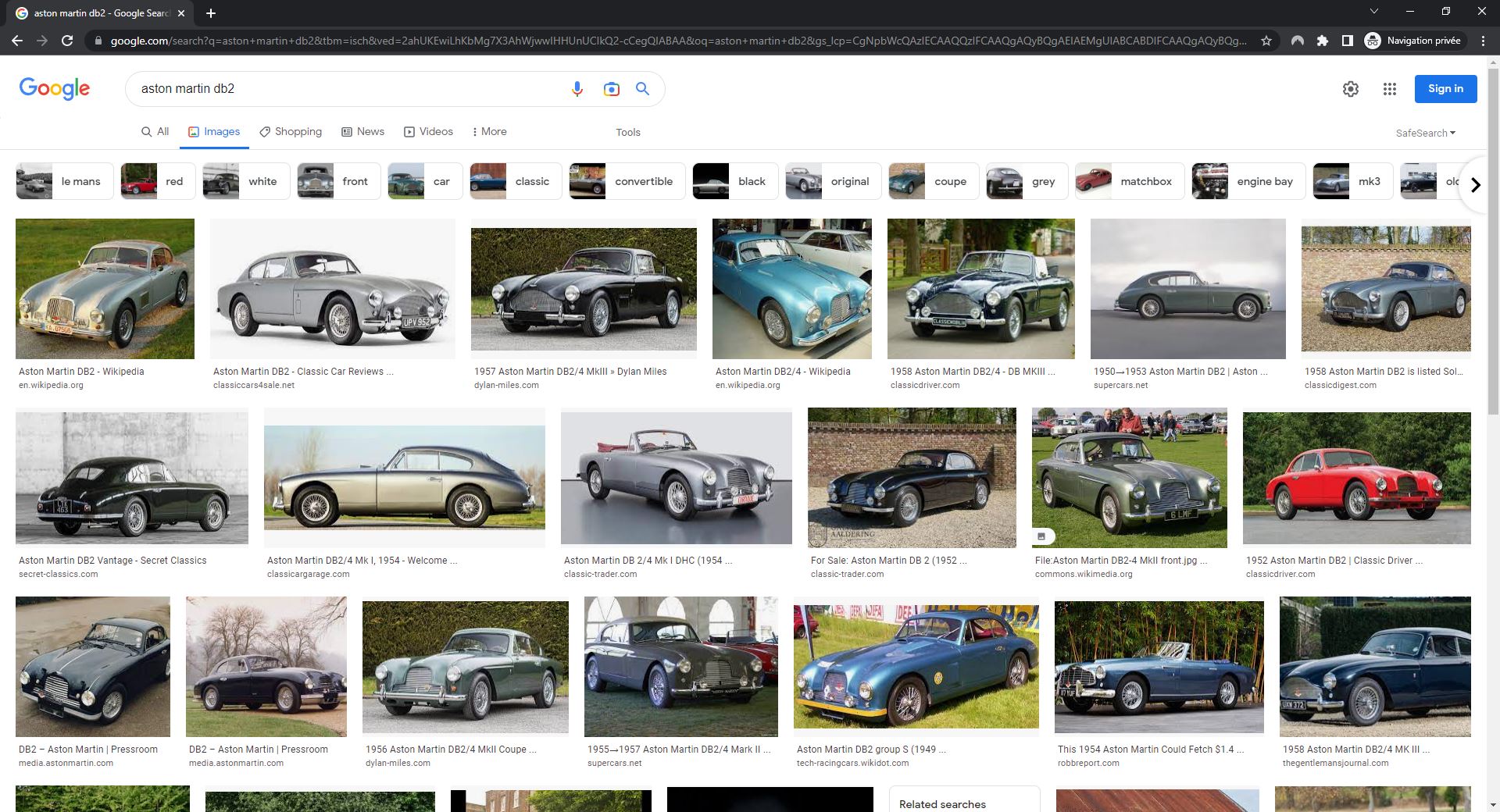
The Google Images results page shows thumbnail previews of images that match the search query. Each result shows a thumbnail image, the website the image is attributed to, and a title (which is often the TITLE tag of the page on which the image was found). A search result can also feature labels giving information on products, copyright license or recipes.
Like web search, results are ranked – the first result being in the top left-hand corner on desktop results. Ranking then goes from left to right and then from top to bottom.
There are a lot more results and websites visible in one screen of Google Images search results than there are in the classic Google search results. A website can still attract clicks even if it is not ranked in the top 10 results. For example, the red car shown in the screen shot below is ranked 13th.
Google Images results pages will often show Related Searches at the top of the page or as a feature as you scroll down the page. These are generated by AI and give an interesting insight into how Google “sees” relationships between different entities. Analyzing these results can help with regular SEO, not just image SEO.
Desktop and mobile results load as users scroll down the page, showing 1000 images before proposing a Show More button.
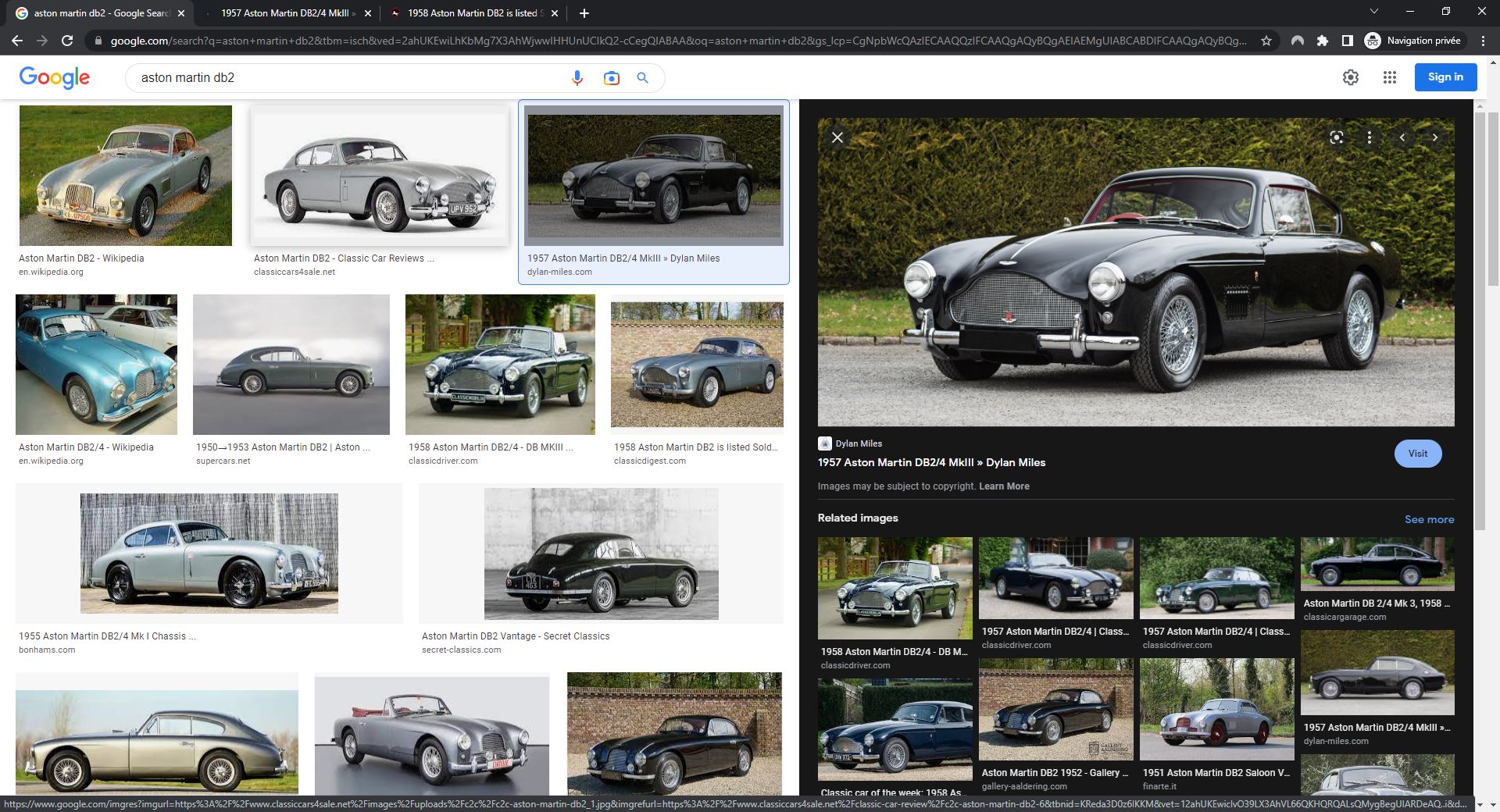
By clicking on a result, the user is not directed directly to the website, but to preview page. This shows a larger version of the image, a longer version of the title and a Visit button. The preview also provides links to previews of similar images. Note that since 2018 there is no longer a View Image button in Google Images.
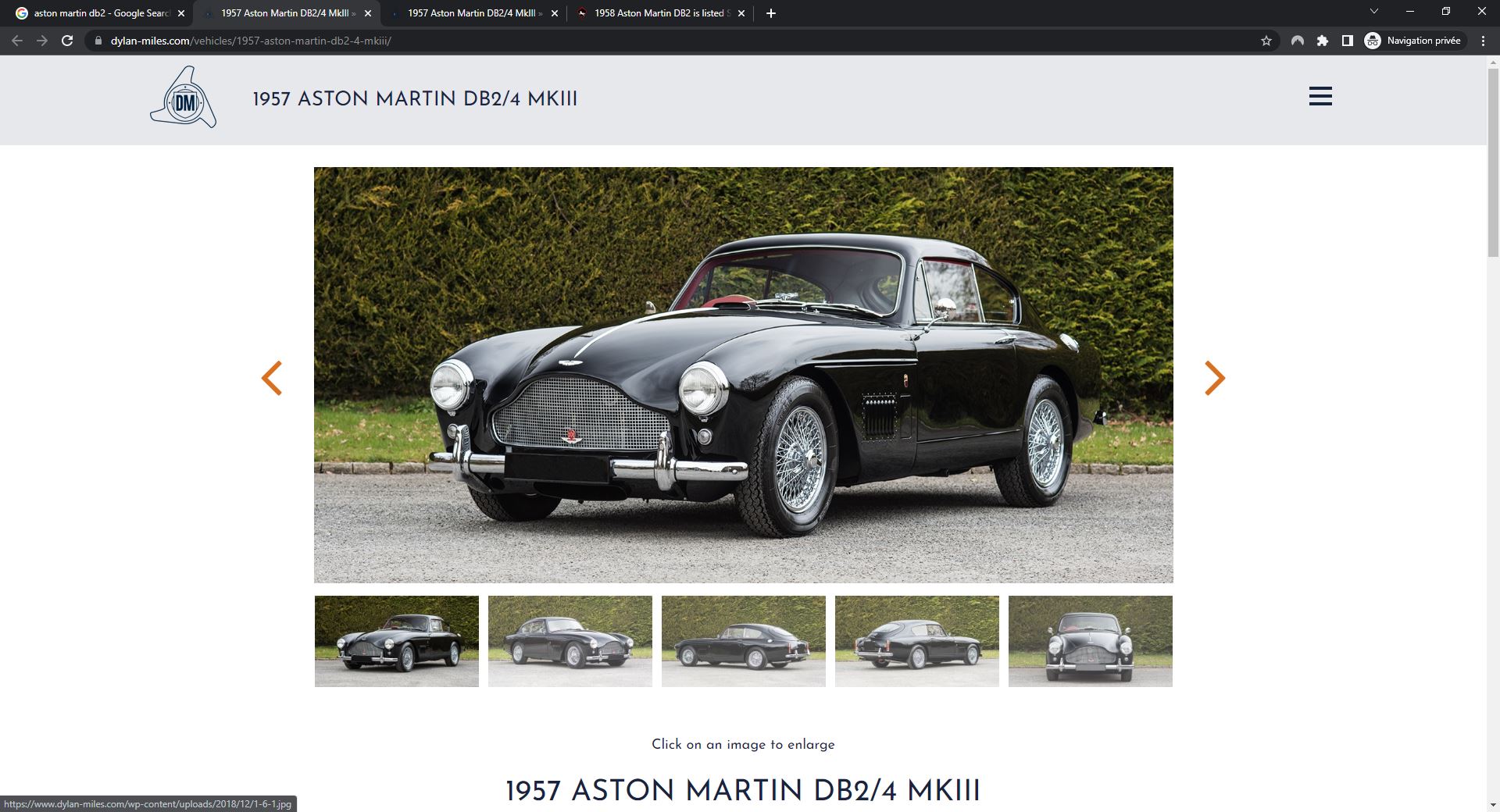
After clicking on Visit, the user will be sent to the page containing the image on the website indicated in the preview. The image shown in search results will often be the most prominent image at the top of the page. In this example, the image that featured in Google Images search results is the first image in a slider at the top of a product page.
Does Google Images generate traffic?
As we have seen above, it is possible for searches to finish with a visit to the website that is associated to an image. However, from the initial search results page, the user needs to click twice – once in the image and again on the image or the Visit button – to get to a website. Click-thru rates are therefore reduced compared to web search.
Click-thru rates will also depend very much on the intention of the searcher. A user searching “Aston Martin DB2” may just want to look at images of this car, but some searchers will also be potential clients for buying the car and they are more likely to visit sites that feature in image search results – especially if the image’s description makes it clear that the car is currently for sale.
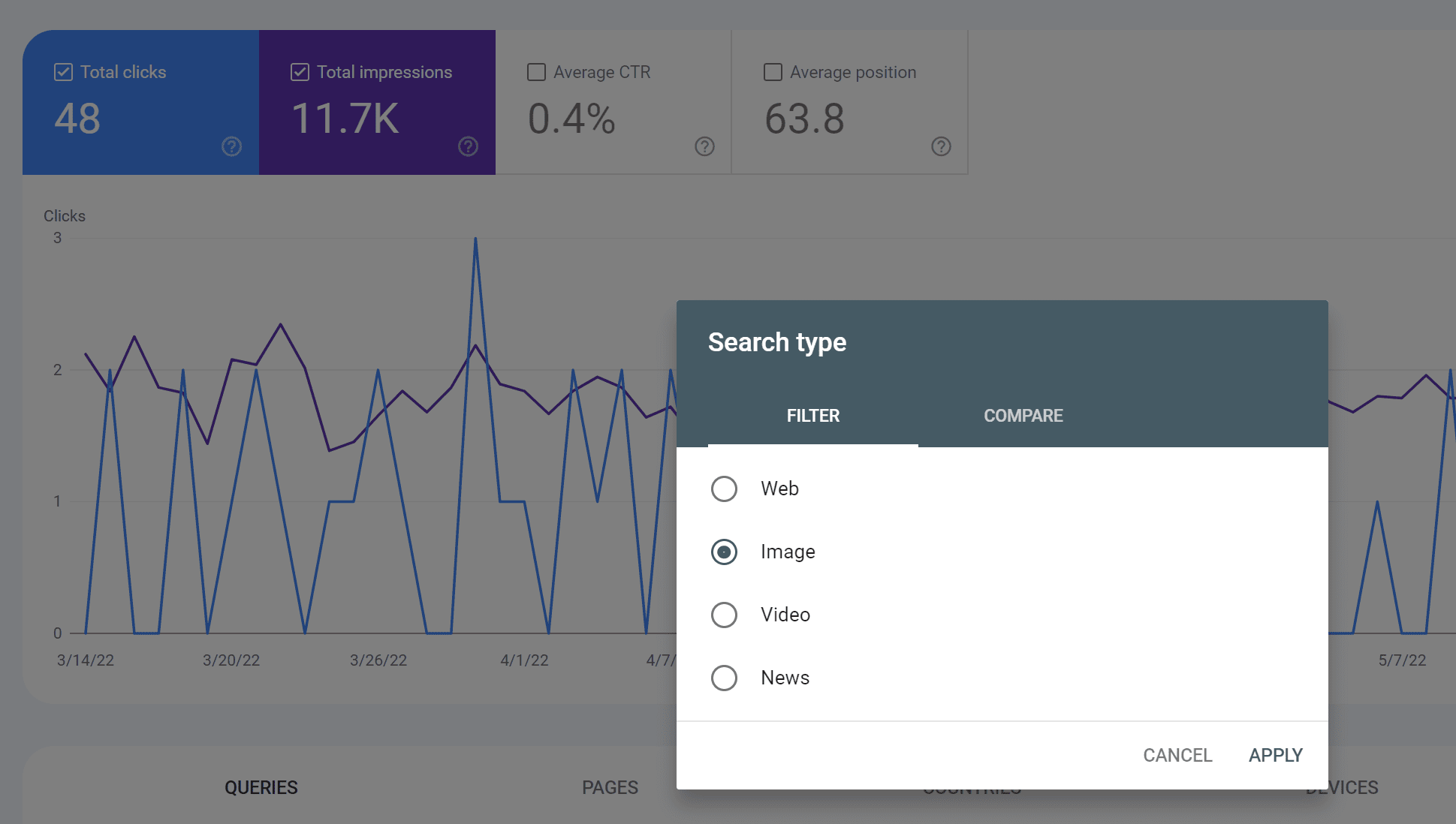
Site owners can check whether image search already drives traffic to their site by using Google Search Console. In the Performance report, it is possible to select “Images” as Search type and view detailed results on queries and traffic generated uniquely from Google Images.
What Google says about image SEO
Google provides detailed guidelines on how images should be formatted and presented in websites. These guidelines have also featured in a Search Engine Lightening Talks video presented by John Mueller. This content provides clues as to how Google ranks images in search results, but also how images can be optimized to provide faster web pages.
The document explains that Google supports images in the following formats: BMP, GIF, JPEG, PNG, WebP, and SVG. WebP is a modern image format created by Google and you may have spotted that PageSpeed Insights often recommend that WordPress sites should use a plugin to automatically convert uploaded images to this format. Using WebP over other image formats will not improve ranking directly, but if the WebP filesize is smaller using it will improve page speed and Core Web Vitals. And Core Web Vitals are part of a ranking signal.
The other important point to take away from Google’s recommendations is that using generic images to illustrate posts may not bring much SEO value. Images already used elsewhere (stock photography for example) will have little chance of ranking for your page in Google Images.
Google’s advice is therefore to produce original images that add value to the written content of the page. It is also very important to continue providing text to rank images. Although Google has advanced in image recognition, the search engine still relies on written content to rank images in Google Images search results.
The full recommendations from Google’s guidelines are
- Provide context. Provide text as context for the image. Make sure that keywords (what users are searching for) are used on the page containing the image. Specifically in page titles and headings.
- Image placement. Place images near relevant text and provide a caption. Consider placing the most important images at the top of the page.
- Write text on the page and not in the image. Don’t embed important text inside of images. Don’t use images as titles or headers of pages.
- Use ALT attributes. Good for accessibility and search engines, ALT text provides information about the image for users who can’t see the image. Google is one of these users.
- Use high-quality images. Images that produce sharp thumbnail previews will attract more traffic.
- Make high-quality sites. Page content quality will be taken into consideration when ranking images and text may be extracted from content to generate text snippet.
- Make sure the site works on mobile and desktop. Because most image searches are performed on mobile, it is important that the site works well on mobile. Use Google’s Mobile-Friendly testing tool.
- Use good, stable descriptive URLs. Google uses the URL path and filename to help understand images. The guidelines state “For example, my-new-black-kitten.jpg is better than IMG00023.JPG”. If you localize your website to another language, make sure you translate filenames, too.”
- Provided relevant structured data. Depending on the content use structured data schema such as Recipe, News Article or Product.
- Large image previews. Allow Google to provide large image previews by using the max-image-preview:large meta robots tag
- Use markup for image licensing. Using structured data on the page or in meta data in the image file.
- Consider speed. Because images are often the elements that take the longest to download, optimize the image file size, apply lazy-loading techniques, use responsive images.
- Provide image site maps to help Google index all the images of your website.
In the next chapter we will look at how you can apply these recommendations for image SEO in WordPress.
Next steps
Introducing our featured blog post series on Image SEO! Dive into the fascinating world of optimizing images for search engines and enhance your website’s visibility. Visit our ebook “More Visibility with Image SEO” and read our featured blog posts on Image SEO to take your website’s visual content to the next level.
- How to Optimize an Image for SEO in WordPress
- How to Get Badges in Google Images Search Results
- An Image Can Sell a Thousand Cars
- Learn how to write alternative text for images with 10 ALT text examples




