If you are sitting there reading this and thinking about creating your first site, I hope you have a clear idea of why you want to invest time and money on such a project and what your return on investment will be. Common objectives for a new website are creating brand awareness, monetizing traffic, generating leads or selling products.
If you are thinking of building an online store, for example, you will expect traffic to your store to convert into revenues that will quickly pay back the investment required to create and host a website. Bear in mind though that your store may need 100 visitors to make one sale (a 1% conversion rate is common for eCommerce sites). We often think of visitors as going through a sales funnel. For 100 people who visit your site, maybe only 50 will visit a product page, 10 will add the product to a shopping cart and then only one in ten will complete the checkout process to complete the purchase.
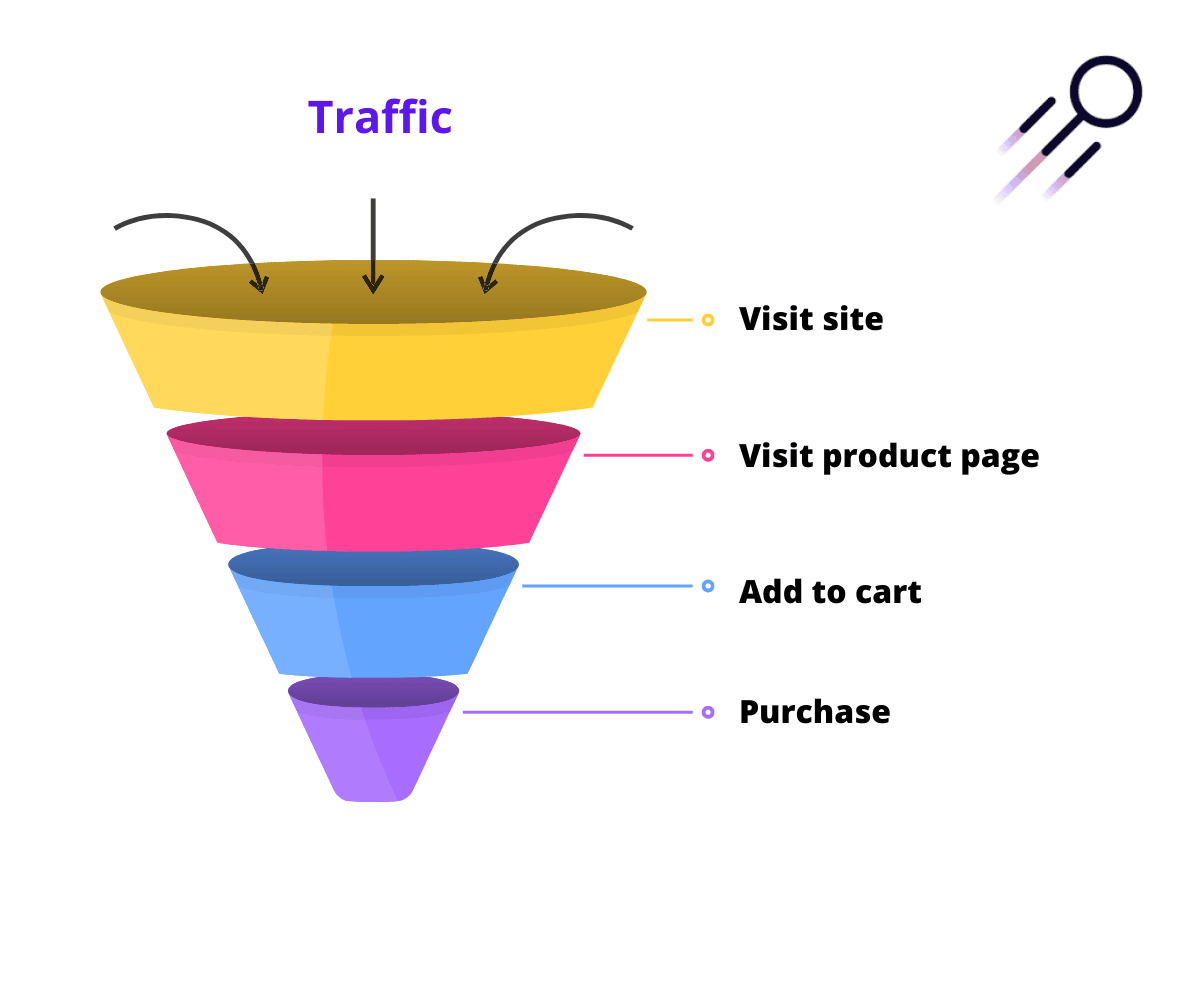
Objectives for your new website
Before you start building your site, I suggest you write down your objectives. An online store is expected to generate online sales and revenues. Our fictive example of a fitness gym in Bristol, Vegas Fit Zone, may also have the objective of selling membership online, but a more realistic objective for them will be to generate inquiries (leads) that will convert to membership sales later. Generating leads is a common objective for many B2B industry sites. A blog with recipes for Indian food may have the objective of monetizing traffic to their site through ads provided by Google AdSense or affiliation.
At this stage you may also want to put figures on those objectives. Examples could be I want my site to generate $10,000 in sales per month, to provide 5 leads a day, to make $100 per month in ad revenue and so on. Try and imagine what your sales funnel will look like from the traffic entering your site to converting as a revenue.
For the examples given above, you may need to generate at least 10,000 visits per month to your new website to meet your objectives. Where is this traffic going to come from? There are many alternatives, but Google is usually the most important source of traffic to any site. This is why SEO is so important. SEO – Search Engine Optimization – is the work you will do to ensure that your site is visible in Google when people search for you by your name or the products, services or information you provide. By doing good SEO, you can generate traffic and revenues 24/7 thanks to your website.
Using personas
Before designing your site and doing keyword research for SEO, it is a good idea to determine who you are building the website for. You can use persona templates to describe your typical client. Knowing who your clients are will help guess what they will type into Google. By noting your typical client’s frustrations and motivations, you can get insights into how they search on Google. You will get ideas about what content will interest your clients and what channels will be useful for targeting them.
SEO features that you will need for a new site
After noting your objectives and describing one or several personas, you can list the features that you want your site to have. Again, think of this from the perspective of your buyer personas. You could note here features like a shopping cart, contact forms, appointment calendars, a map showing the location of your store, videos, photo gallery, etc.
There are many things you could add, but we will concentrate on features that are the most important for your SEO.
- SSL / HTTPS – Your site should be hosted with security certificate, meaning that the URLs of pages start with “https:” and not “http:”. This is a ranking factor.
- Responsive design and mobile friendliness – Your site should display correctly whatever size device (computer, tablet, phone) it is viewed on. Google only reads the mobile versions of sites.
- Page speed – make sure that the site is designed respect Google’s Core Web Vitals that set thresholds on what is good or poor page speed.
- About page – Your site should have an easy to find About page that informs users about who you are and what the website is about. You should also assure that the person or company responsible for the site is clearly identified.
- Blog – for long-term SEO your site should enable you to publish new content regularly. The blog format (with authors, publication dates, categories, etc.) is particularly good for SEO and you should have it as a feature whether you open the blog or not when you initially launch your site. Blog posts can be very useful as “lead magnets” for many sites.
- Product / service pages – Unless you are just building a blog, you should plan for a distinct page per product (or service) rather than listing all your products on a “Our products” page.
- Menu – Not to be confused with a restaurant menu, a website menu is a list of links that helps users navigate through different pages or sections of a website. This will help users and Google discover all the pages on your site.
- Sitemap – Your site should also generate a sitemap file that you can submit to Google and other search engines. This will help Google see changes to your website more quickly.
- H1, H2, Hn title structure – tThe pages of your site should correctly use header tags to show titles. Headings, especially the main H1 title should be clearly visible on every page.
- TITLE and META Description tag editing – Make sure that the CMS (Content Management System) that you will use to manage your site allows you to edit TITLE and META Description tags for every page. These tags are very important to Google.
- Image ALT tag editing – Images are an important part of SEO. You should ensure that your CMS allows you to edit the ALT attribute of images. Other features that are nice to have for image SEO are image compression and renaming filenames.
- Breadcrumbs – Every page should have breadcrumb links allowing users to navigate back up the structure of the site. For example, the breadcrumbs for a product page would allow you to navigate back to the home page, the store page and the product category page.
- Descriptive URLs – Your CMS should allow you to create URLs that describe the structure of your site like breadcrumbs. For example, https://example.com/store/my-category/my-product/.
- 301 Redirections – because you will change URLs over time, it is important that your CMS has a feature to add redirections form old URLs to new URLs to ensure that you don’t lose traffic when the address of a page changes.
- Structured data Schema.org – Modern sites must have the capability of adding structured data to your pages. Structured data defined by Schema.org and recognized by Google helps the search engine understand what pages are about. Examples of recognized Schema are Products, LocalBusiness, Recipe, Video, Job, Evens, How-To and FAQ.
- HREFLANG – If you want to publish in more than one language, your CMS must support HREFLANG. This tag allows Google to understand which audience is targeted by what part of your site.

SEO site structure with keywords
Finishing the strategic design of your website it is good to complete your list of features with a document listing the sections and pages you want and their organization as a menu. You can use a spreadsheet to list the pages in the order of their appearance in the menu (see the example below).
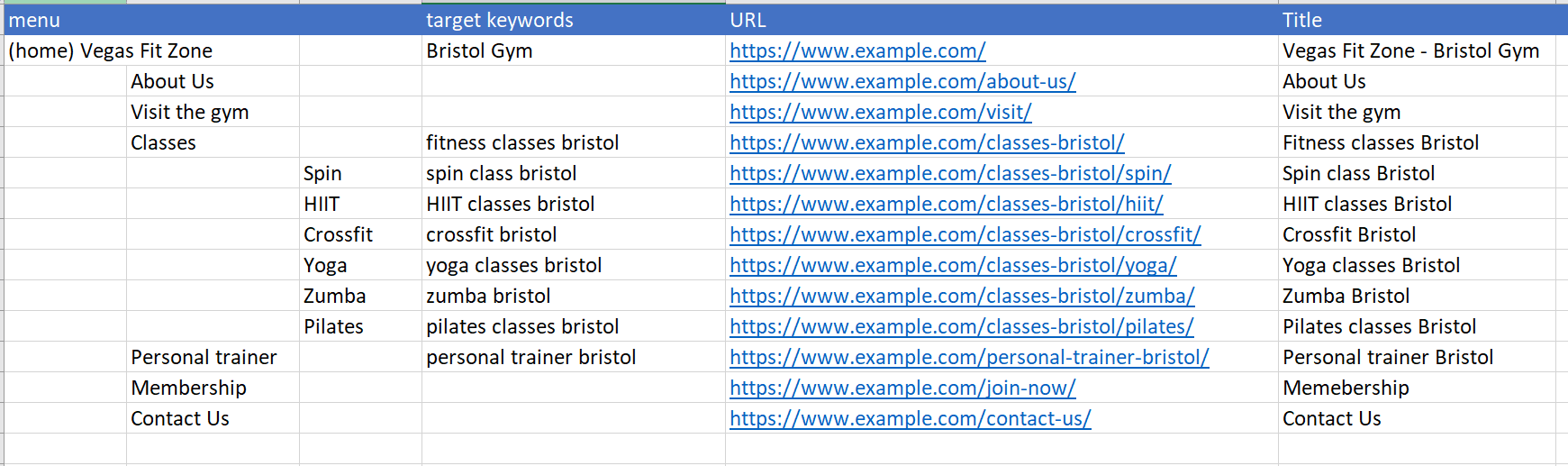
To help with the terminology you will use for navigation and page titles, spend time doing keyword research first. Keywords are popular search terms that you want to rank for in Google.
See our eBook Keywords and SEO, Everything You Need to Know for a full guide to finding keywords and learn how to do keyword research like the pros!
Keyword research will help you choose the best titles for pages and menus (this is your first SEO job and it is better to do it now, before building the site rather than after the site is launched).
At this stage you should also start thinking seriously about the feasibility of your project. Does keyword research show that there is a sufficient volume of search in Google to provide the traffic you need to meet your objectives? If you have not found any good keywords or if search volumes are very low, then SEO may not be the most important strategy for your generating traffic for your website!
Imagining that the results of your keyword research are positive, you can add your finished website structure to the document containing your objectives and the features that you would like your site to have (taking into account the features that we recommended for SEO). Once you have this document, you can decide about what CMS you will use to build your site and then you can start building it or get a professional in to help! The next chapter deals with choosing the best CMS for SEO. Read this even if you plan on getting someone else to develop your site, because you will need to be able to use your CMS to do SEO work later.



