Google released a Helpful Content update in September on the heels of a Core Update (last year it was the other way around). Strangely, though, the announce of these two updates coincided with relative calm on volatility reports from rank-tracking software, suggesting that changes only targeted certain niches rather than all websites. A pattern of websites affected by the Helpful Content Update seems to be emerging from research by the SEO community suggesting that recipe and travel blogs are among the hardest hit. Meanwhile, Google is also on trial in the USA and both the final verdict and leaks from the courtroom may have damaging consequences for the search engine.
September 7th – End of August 2023 Core Update
Released in August (see our Google SEO news from last month), the August 2023 Core Update finished rolling out on September 7th.
Core Updates happen a few times per year, the previous one was in March 2023, and they concern the overall quality of sites. Google does not release specific information about what signals are used in Core Updates, but its advice from 2019 was to “Get to know the quality rater guidelines and E-A-T”. You can read more about this advice in our article Optimizing WordPress sites for Google EAT.
If you suffered ranking drops during the period from August 22nd to September 7th, it is probable that this was caused by this Core Update. By optimizing your site to improve EAT, you can earn rankings back over time, most probably when the next Core Update happens.
September 14th – September 2023 Helpful Content Update
Google announced the release of the September Helpful Content update on September 14th through a post by @googlesearchc on X with the message “The September 2023 helpful content update is rolling out with an improved classifier” and a link to the Google Search Status Dashboard.
This was followed by two further posts to indicate that documentation about Helpful Content had been updated. The page “Google Search’s helpful content system and your website” has been updated with new guidance about hosting third-party content and the page “Creating helpful, reliable, people-first content” now features new points to consider about removing content and changing dates. This includes the suggestion that website owners should not be changing the dates of blog posts to make them seem fresh when no significant change has been made.
Google update specialist, Mary Haynes, created a useful post on X with things you need to know about the Content Helpful update. She reminds us that the Helpful Content system is a machine learning system that aims to better reward content that provides visitors with a satisfying experience. Pages are rated for helpfulness and too many poor, unhelpful pages can see a whole site classified as “unhelpful” which is a negative signal for ranking. Her early theory was that the September Helpful Content update implemented signals related to the Experience factor – Experience is the first “E” in the abbreviation E-E-A-T used in the Google Quality Raters Guidelines in December 2022.
Sites classified as unhelpful after this update may see a sudden drop in traffic to their website from Google. It is believed that these sites will remain classified as unhelpful (and loose ranking) until the next Helpful Content update when each site will be re-evaluated.
Marie has set up a form for website owners to submit their site for review if they think they were impacted by this update. She promises to share information with all those that contribute and has already reported that niche sites and recipe bloggers seemed to be particularly affected by this update.
In a separate study, Lily Ray (an prominent SEO professional based in New York) has found that the sites the most negatively hit by the update were online tools (like calculators, converters, alarms, etc.), information sites (city data, definitions, meanings of colors, etc.), lifestyle sites (horoscopes, meanings of numbers, self-improvement, motivational quotes, etc.) and travel blogs.
The Helpful Content Update stopped rolling out on September 27th. If you lost ranking between September 14th and September 27th, you were probably hit by this update and we suggest you refer to the self-assessment questions in Google’s article “Creating helpful, reliable, people-first content”.
Update to Language Matching Systems
In a blog post published on September 8th, Google announced that it had released several updates over the past few months to improve the way that users’ multiple languages are taken into account in search results. This will particularly impact countries and regions where people commonly speak and search in more than one language.
This means that Google has moved away from determining language strictly form OS or browser settings and will be able to mix results in different languages within the same search results. Users who wish to force results into a single language are invited to use the language filter.
In the same article, Google encourages publishers to cater for as many languages as possible, rather than just concentrating on one language that they assume is widely understood. It points publishers to documentation on the HRFLANG attribute as the correct way of indicating language and region to Google. Our article on this subject we’ll tell you, “All You Need to Know About Creating a Multilingual WordPress Site”.
Revelations about algorithms during Google antitrust trial
Since September 12th, Google has been on trial in Washington, DC, with the US Justice Department accusing the company of rigging the internet search market and abusing its power and resources to maintain a monopoly. It is expected that trial will last until the end of the year and that it will result in Google having to restructure its company in the US to respect antitrust laws.
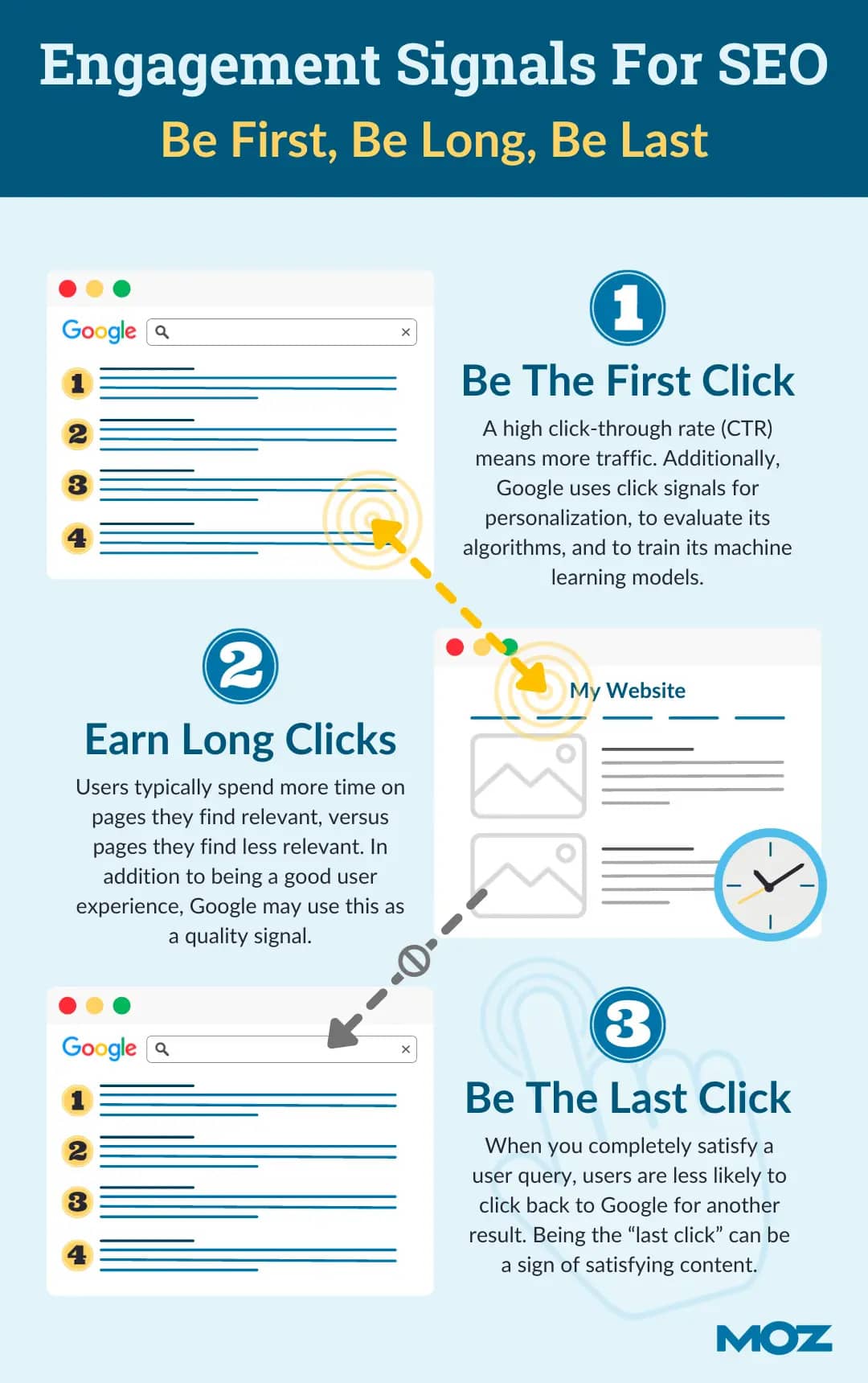
Although the hearing is behind closed doors, information is leaking from proceedings, including the testimony of former Google employee Eric Lehman who, according to reporting by the @BigTechOnTrial X account, stated that Google does use click data as part of its ranking algorithms. In the testimony Lehman says that Google avoids communicating on this fact to discourage SEOs from manipulating results.
In a 2021, Cyrus Shepard of Moz, speculated on how Google could use click data and how websites could optimize for this factor in an article entitled “3 Vital Click-Based Signals for SEO: First, Long, & Last.” His advice is resumed in this infographic can now be considered as sound advice.
Robot.txt commands to block Google Bard
Google announced on September 28th that website publishers now have the possibility of blocking Bard or other AI tools (like Vertex AI) from crawling their websites using the robot.txt file. The crawler working for AI tools will be distinct from those used by Google Search and can be blocked from reading a website with the following commands in robots.txt:
User-agent: Google-Extended Disallow: /
This follows from an initiative already taken by Open AI to allow sites to block ChatGPT by using the following commands:
User-agent: CCBot Disallow: / User-agent: GPTBot Disallow: /
Bing Chat, on the other hand, proposes an alternative method to prevent Bing from using website content in AI-generated responses. Their method consists of using the NOARCHIVE and NOCACHE attributes in the ROBOTS META tag in each page. They say that these attributes are not used by Bing Search. However, NOCACHE is used by Google Search and will indicate that Google should not show a cached version of a page in search results.
We recommend thinking hard about whether you want to block AI from reading your content before adding these commands to your website. Most websites publishers will probably want to feature in the links suggested by Bing Chat, Bard or SGE.



